PROCESS
Problem solving through designDesign Thinking is a solution-based approach to solving problems. This approach to problem solving starts with a solution in order to begin defining enough of the parameters to optimize the path to the goal. The solution, using this methodology, is actually the starting point.
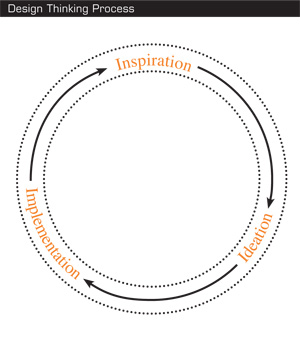
Design projects must ultimately pass through three phases (see the exhibit “Inspiration, Ideation, Implementation”). We label these “inspiration,” for the circumstances (be they a problem, an opportunity, or both) that motivate the search for solutions; “ideation,” for the process of generating, developing, and testing ideas that may lead to solutions; and “implementation,” for the charting of a path to market. Projects will loop back through these phases—particularly the first two—more than once as ideas are refined and new directions are taken.


INSPIRATION
OpportunityWhat’s the business problem? Where’s the opportunity?
Global water reserves and access to pure water is diminishing globally. Opportunities exist in all sectors of the water space (e.g., agriculture, water treatment, emergency relief)
ObservationLook at the world: Observe what people do, how they think, and what they need and want.
Observations of the Middle East and South Asia: High levels of water stress and limited water supplies for households throughout both regions, including Jordan, Israel, Saudi Arabia, India, and Bangladesh.
What people rely on: Water deliveries by local water distributors on a weekly basis. Attempt to manage water resources for daily activities while often running out of water.
What people need: An alternative water supply that is abundant and not dependent on water deliveries or governmental rationing.



IDEATION
Brainstorming
Involves many disciplines from the start (e.g., engineering and marketing).
Immerse Global founders realized the need for water generation applications that would use the atmosphere as an alternative water source, and worked with Stanford University to develop such alternatives.
Engineers explored a series of solution paths, including Water Deliver Applications, Ventilation Technologies, Vapor Extraction, and User Interface.
Rapid PrototypingAt the heart of the process is the notion that in order to innovate, one must understand the needs of the user, and the context surrounding the design. Unlike many other design and development processes, this is cyclical. The iterative nature assures that teams are not stuck on one idea for too long, and that ideas are being continuously tested through rapid prototyping and testing.
“Fail early and fail often so you can succeed faster,” is one of the mantras for rapid prototyping. – IDEO


IMPLEMENTATION
Execute The Vision
Engineer the final prototype and proceed to final product design
Expect Success!
